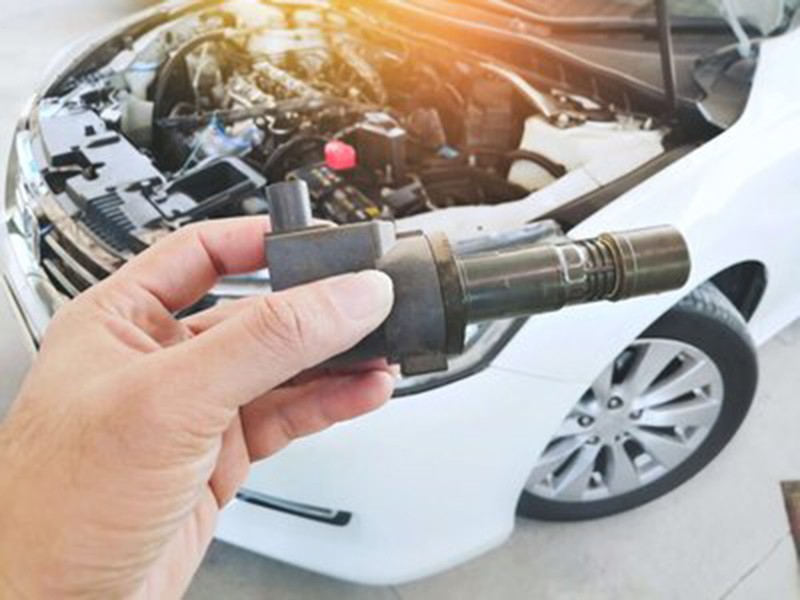
Issues with the Ignition Coil, Signs, and Resolutions
The ignition coil is an electrical component that converts the low voltage from the battery to the high voltage necessary to create the spark in the engine's combustion chamber. This spark ignites the air/fuel mixture, running the engine for an ignition start.
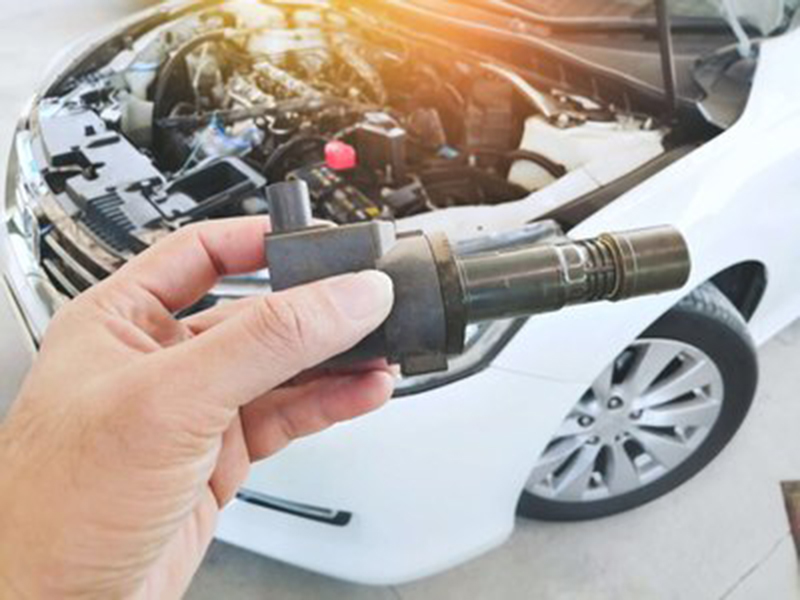

Ignition coil problems can result in poor engine performance and even prevent your vehicle from starting. Here are some common symptoms of ignition coil issues and solutions:
Symptoms:
Engine misfires or runs rough
Difficulty starting the engine
Stalling or hesitation during acceleration
Decreased fuel efficiency
Illuminated check engine light
Engine backfires
Rough idle or shaking at low speeds
Loss of power while driving
Overheating or high engine temperature
Unusual smells coming from the engine
Solutions:
Replace faulty ignition coils
Check and replace worn spark plugs and wires
Inspect and clean battery connections
Check and repair damaged wiring or connectors
Use a scan tool to diagnose any underlying issues with the ignition system
Replace damaged or worn-out ignition coils
Check and replace clogged fuel filters
Inspect and replace malfunctioning fuel injectors
Test and replace faulty crankshaft or camshaft position sensors
Ensure proper air intake by checking and cleaning air filters and mass airflow sensors
How to Test an Ignition Coil?
To test an ignition coil, follow these steps:
Turn off the engine and disconnect the battery to ensure your safety.
Locate the ignition coil(s) in your vehicle; they are usually near the spark plugs.
Use a digital multimeter to measure the resistance of the primary and secondary coils by connecting the multimeter leads to the corresponding terminals on the coil.
Compare the readings to the specifications provided by the manufacturer. If the measurements are outside the recommended range, the coil may be faulty and needs replacement.
Check the wiring connections attached to the ignition coil for any signs of damage or corrosion.
Inspect the condition of the spark plugs and replace them if necessary.
Reconnect the battery and start the engine. Observe if there are any changes in engine performance, such as smooth running or improved power delivery.
If you don't have access to a multimeter, you can also perform an "output test" using a spark tester tool. This involves removing the spark plug wire from each spark plug in turn and attaching the spark tester to the end of the wire. Then, crank the engine and observe whether the spark jumps across the tester gap. If there is no spark or the spark is weak, it may indicate a faulty ignition coil.